Difference between revisions of "Complex Systems"
Gianfranco (talk | contribs) |
Gianfranco (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Bookind}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--<languages />--> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
After the previous chapters, we should now be able to recognize that, both in modern physics and in biology, a "Complex System" is a multi-component dynamic system composed of different subsystems that typically interact with each other. Such systems are typically studied through "holistic" investigation methodologies or as "total" computation of the behaviours of the individual subsystems, together with their mutual interactions; these can be described analytically through mathematical models, rather than, in a "reductionist" manner (i.e. by breaking down and analysing the system in its components). Typical of Complex Systems, are the concepts of self-organization and "Emerging Behaviour". | After the previous chapters, we should now be able to recognize that, both in modern physics and in biology, a "Complex System" is a multi-component dynamic system composed of different subsystems that typically interact with each other. Such systems are typically studied through "holistic" investigation methodologies or as "total" computation of the behaviours of the individual subsystems, together with their mutual interactions; these can be described analytically through mathematical models, rather than, in a "reductionist" manner (i.e. by breaking down and analysing the system in its components). Typical of Complex Systems, are the concepts of self-organization and "Emerging Behaviour". | ||
Revision as of 18:37, 30 May 2021
After the previous chapters, we should now be able to recognize that, both in modern physics and in biology, a "Complex System" is a multi-component dynamic system composed of different subsystems that typically interact with each other. Such systems are typically studied through "holistic" investigation methodologies or as "total" computation of the behaviours of the individual subsystems, together with their mutual interactions; these can be described analytically through mathematical models, rather than, in a "reductionist" manner (i.e. by breaking down and analysing the system in its components). Typical of Complex Systems, are the concepts of self-organization and "Emerging Behaviour".
In this chapter we will expose some contents in favour of this more stochastic and complex vision of the neuromotor functions of the masticatory system.
Article by Gianni Frisardi
|
Preliminary Consideration
In recent years, parallel developments in different disciplines have focused on what has been called "Connectivity"; a concept used to understand and describe the "Complex Systems". The conceptualizations and functionalisations of connectivity have evolved widely within their disciplinary boundaries, but there are clear similarities in this concept and in its application across the disciplines. However, any implementation of the concept of connectivity involves both ontological and epistemological constraints, which lead us to wonder if there is a type or set of connectivity approaches that could be applied to all disciplines. In this review, we explore four ontological and epistemological challenges in using connectivity to understand complex systems from the point of view of very different disciplines.
In Chapter ' Connectivity and Complex Systems', we will introduce definitely the concept of:
- defining the fundamental unit for the study of connectivity;
- separate structural connectivity from functional connectivity;
- understanding of emerging behaviour; and
- measuring connectivity.
Now we have to consider the complex profile of the masticatory function, to be able to talk about "connectivity"[1]
Only in later times the importance of the mastication function became evident as a Complex System; it did become clear because of its interaction with a multitude of other Nervous Centers and Systems (CNS), which are also distant from a functional point of view.[2]. The mastication function, indeed, has always been considered a peripheral ad isolated function with reference to the phonetics and chewing. Following this scientific philosophy, there have been countless points of view that focused, and still focus, on the diagnosis and rehabilitation of Mastication exclusively in the maxillaries, by excluding any multi-structural correlation.
This kind of approach denotes a clear 'reductionism' in the contents of the system itself: in biology, it is more realistic to consider the functionality of systems such as "Complex Systems" that do not operate in a linear way. These systems employ a stochastic approach, in which the interaction of the various constituents generates an ‘Emergent Behaviour’ (EB)[3] of the same system.[4]
The paradigmatic result reverses the tendency to consider the masticatory system as a simple kinematic organ, and goes well beyond the traditional mechanistic procedure of Classical Gnathology.
This aspect also introduces a type of indeterministic profile of biological functions, in which the function of a system presents itself as a network of multiple related elements. In addition to interpreting its state, this system should be stimulated from the outside to analyse the evoked response, as it is typical of indeterministic systems.[6]
It is, therefore, essential to switch from a simple and linear model of dental clinic to a Stochastic Complex model of masticatory neurophysiology.
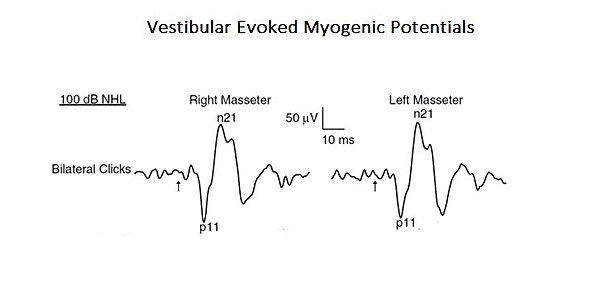
As a confirmation of this more complex and integrated approach to interpret the functions of mastication, a study is presented here where the profile of a "Neural Complex System" emerges. In the mentioned study, the organic and functional connection of the vestibular system with the trigeminal system was analysed. [7]. Acoustic stimuli may evoke EMG-reflex responses in the masseter muscle called Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (VEMPs). Even if these results were previously attributed to the activation of the cochlear receptors (high intensity sound), these can also activate the vestibular receptors. As anatomical and physiological studies, both in animals and humans, have shown that masseter muscles are a target for vestibular entrances, the authors of this study have reassessed the vestibular contribution for the masseteric reflexes. This is a typical example of a base-level complex system as it consists of only two cranial nervous systems but, at the same time, interacting by activating mono- and polysynaptic circuitry (Fig. 1).
It would be appropriate at this point to introduce some topics related to the above mentioned concepts, which would clarify the rationale of the Masticationpedia project. This would introduce the chapters which are at the core of the project.
Hence, the object is:
Mastication and Cognitive Processes
In recent years, mastication has been a topic of discussion about the maintenance and support effects of cognitive performance.
An elegant study performed through fMR and positron emission tomography (PET) has shown that mastication leads to an increase in cortical blood flow and activates the additional somatosensory cortex, motor motor and insular, as well as the striatum, the thalamus, and the cerebellum. Mastication right before performing a cognitive task increases oxygen levels in the blood (BOLD of the fMRI signal) in the prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus, important structures involved in learning and memory, thereby improving the performance task..[8] Previous epidemiological studies have shown that a reduced number of residual teeth, incongruous use of prosthetics, and a limited development of the mandibular force are directly related to the development of dementia, further supporting the notion that mastication contributes to maintaining cognitive functions.[9].
A recent study[10] has provided further evidence in support of the interaction between masticatory processes, learning and memory, focusing on the function of the hippocampus that is essential for the formation of new memories. An occlusal disharmony, such as loss of teeth and increases in the vertical occlusal dimension, causes bruxism or pain to the mastication muscles and temporomandibular disorders (TMDs).[11][12]. Hence, to describe the impaired function of the hippocampus in a reduced situation or abnorme asticatory function. Tthe authors employed an animal model (mice) called ‘Molarless Senescence-Accelerated Prone’ (SAMP8) in order to make a parallelism on man. In mice, SAMP8, to which the occlusion was modified, increasing the occlusal vertical dimension of about 0.1 mm with dental materials showed that the occlusal disharmony disrupts learning and memory. These animals showed an age-dependent deficit in space learning in the mice at Morris’s water. [13][14]
Increasing the vertical dimension of the bite in SAMP8 mice decreases the number of pyramidal cells[14] and the numbers of their dendritic spines.[15] It also increases the hypertrophy and hyperplasia fibrillar protein acid in astrocytes in the regions of the CA1 and CA3 hippocampus.[16]. In rodents and monkeys, occlusal disharmonies induced through an increase in the vertical dimension with acrylic increases on the incisors [17][18] or the insertion of bite-plane in the jaw are associated with increased urinary cortisol levels and elevated plasma levels of corticosterone, suggesting that occlusal disharmony is also a source of stress.
In support of this notion, SAMP8 mice with learning deficits show a marked increase in the plasma levels of corticosterone [12] and subregulation of GR and GRmRNA of the hippocampus. The occlusal disharmony also affects catecholaminergic activity. Alternating the closure of the bite by inserting an acrylic bite-plane on the lower incisors leads to an increase in levels of dopamine and noradrenaline in the hypothalamus and the frontal cortex[17][19],and decreases in thyroxinaydroxylase, GTP cyclohydrochloride, and immunoreactive serotonin in the cerebral cortex and the caudate nucleus, in the nigra substance, in the locus ceruleus, and in the dorsal raphe nucleus, which are similar to chronic stress-induced changes.[20] These changes in the catecolaminergic and serotonergic systems, induced by occlusal disharmonies, clearly affect the innervation of the hippocampus. The conditions of increasing the vertical dimension alter neurogenesis and lead to apoptosis in the ippocampal gyrus by decreasing the expression of the ippocampal brain derived from neurotrophic factors: all this could contribute to the changes in observed learning in animals with occlusal disharmony.[10]
Brainstem and Mastication
The brainstem district is a relay area that connects the upper centres of the brain, the cerebellum, and the spinal cord, and provides the main sensory and motor innervation of the face, head, and neck through the cranial nerves.
This plays a determining role in regulation of respiration, locomotion, posture, balance, excitement (including intestinal control, bladder, blood pressure, and heart rate). It is responsible for regulating numerous reflexes, including swallowing, coughing, and vomiting. The brainstem is controlled by higher Cerebral Centers from cortical and subcortical regions, including the Basal Ganglia Nuclei and Diencephal, as well as feedback loops from the cerebellum and spinal cord. Neuromodulation can be achieved by the ‘classical’ mode of glutammatergic neurotransmitters and GABA (gamma-amino butyric acid) through a primary excitation and inhibition of the ‘anatomical network’, but can also be achieved through the use of transmitters acting on G-proteins. These neuromodulators include the monoamine (serotonine, noradrenaline, and dopamine) acetylcholine, as also glutamate and GABA. In addition, not only do neuropeptides and purines act as neuromodulators, so do other chemical mediators like Growth Factors which, too can have similar actions..[21]
The neural network described above does not end with the only correlation between trigeminal somatosensory centres and other motor areas but also strays into the amigdaloidei processes through a correlation with the trigeminal brainstem area. The amygdala becomes active from fear, playing an important role in the emotional response to life-threatening situations. When lab rats feel threatened, they respond by biting ferociously. The force of the bite is regulated by the motor nuclei of the trigeminal system and trigeminal brainstem Me5. The Me5 transmits proprioceptive signals from the Masticatory muscles and parodontal ligaments to trigeminal nuclei and motors. Central Amygdaloid Nucleus (ACe) projections send connections to the trigeminal motor nucleus and reticular premotor formation and directly to the Me5.
To confirm this, in a study conducted among mice, the neurons in the Central Amigdaloide nucleus (ACe) were marked after the injection of a retrograde tracer(Fast Blue), in the caudal nucleus of the Me5, indicating that the Amigdaloians send direct projections to the Me5, and suggest that the amygdala regulates the strength of the bite by modifying the neuronal activity in the Me5 through a neural facilitation..[22]
Modifying occlusal ratios can alter oral somatosensory functions and the rehabilitative treatments of the Masticatory system should restore somatosensory functions. However, it is unclear why some patients fail to adapt to the masticatory restoration, and sensomotor disorders remain. At first, they would seem to be structural changes, not just functional ones. The primary motor cortex of the face[10] is involved in the generation and control of facial gold movements and sensory inputs or altered motor functions, which can lead to neuroplastic changes in the M1 cortical area. [23]
Conclusive Consideration
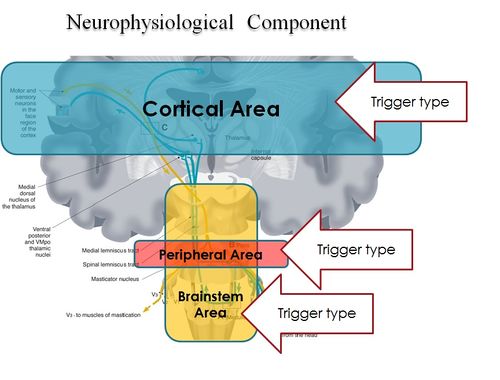
In conclusion, it is clear from the premise, that the Masticatory system should be considered not certainly as a system simply governed by mechanical laws, but as a "Complex System" of indeterministic type, where one can quantify the "Emerging Behavior" only after stimulating it and then analysing the response evoked (Fig. 2). The Neuronal System also dialogues with its own encrypted machine language (potential action and ionic currents) and, therefore, it is not possible to interpret the symptoms referred to by the patient through natural language. This concept deepens knowledge of the state of health of a system because it elicits an answer from the inside—or, at least, from a large part—of the network by allocating normal and/or abnormal components of the various nodes of the network. This concept, in scientific terms, introduces a new paradigm in the study of the Masticatory System, titled "Neuro Gnathology Funtional" that we will meet in due course in the chapter ‘Extraordinary Science’.
Currently, the interpretation of the Emergent Behavior of the Mastication system in dentistry is performed only by analysing the voluntary valley response, through electromyographic recordings ‘EMG interference pattern’, and radiographic and axographic tests (replicators of mandibular movements). These can only be considered descriptive tests.
The paradigm of gnathological descriptive tests faced a crisis years ago and, despite an attempt to reorder the various axioms, schools of thought, and clinical-experimental strictness in the field of Temporomandibular Disorders through the realization of a protocol called "Research Diagnostic Criteria" RDC/TMDs, it has not yet come to accept this paradigm for the scientific-clinical incompleteness of the procedure itself. It deserves, however, a particular reference to the RDC/TMD, at least for the commitment that was carried out by the authors and, at the same time, to scroll the limits. The RDC/TMD protocol was designed and initialized to avoid the loss of ‘standardized diagnostic criteria’ and evaluate a diagnostic standardization of empirical data at disposition. This protocol was supported by the National Institute for Dental Research (NIDR) and conducted at the University of Washington and the Group Health Corporative of Puget Sound, Seattle, Washington. Samuel F. Dworkin, M. Von Korff, and L. LeResche [24] were the main investigators.
To arrive at the formulation of the protocol of the ‘RDC’, a review of the literature of diagnostic methods in rehabilitative dentistry and TMDs, and subjected to validation and reproducibility, has been made. Taxonomic systems were taken into account by Farrar (1972)[25][26] Eversole e Machado (1985)[27], Bell (1986)[28] Fricton (1989)[29], American Academy of Craniomandibular Disorders (AACD) (1990)[30], Talley (1990)[31], Bergamini e Prayer-Galletti (1990)[32], Truelove (1992)[33], and compared them by granting them to a set of assessment criteria. The evaluation criteria were divided into two categories that involve methodological considerations and clinical considerations.
The end of the research came to the elimination, due to a lack of scientific and clinical validation, of a series of instrumental diagnostic methodologies like interferential electromyography (EMG Interference Pattern), Pantography, X-ray diagnostics, etc. These will be described in more detail in the next editions of Masticationpedia. This first target was, therefore, the scientific request of an "objective data"' and not generated by opinions, schools of thought or subjective evaluations of the phenomenon’. During the Workshop of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR) of 2008, preliminary results of the RDC/TMDs were presented in the endeavour to validate the project. The conclusion was that to achieve a review and simultaneous validation of [RDC/TMD], it is essential that the tests should be able to make a differential diagnosis between TMD patients with pain and subjects without pain, and above all, discriminate against patients with TMD pain from patients with orofacial pain without TMD.[34]
This last article, reconsidering pain as an essential symptom for the clinical interpretation, puts all the neurophysiological phenomenology in the game, not just this. To move more easily in this medical branch, a different scientific-clinical approach is required, one that widens the horizons of competence in fields such as bioengineering and neurobiology.
It is, therefore, essential to focus attention on how to take trigeminal electrophysiological signals in response to a series of triggers evoked by an electrophysiological device, treating data and determining an organic-functional value of the trigeminal and masticatory systems as anticipated by Marom Bikson and coll. in their «Electrical stimulation of cranial nerves in cognition and disease».
We should think of a system that unifies the mastication and neurophysiological functions by introducing a new term: "Neuro-Gnathological Functions" which will be object of a dedicated chapters.
- ↑ Turnbull L, Hütt MT, Ioannides AA, Kininmonth S, Poeppl R, Tockner K, Bracken LJ, Keesstra S, Liu L, Masselink R, Parsons AJ, «Connectivity and complex systems: learning from a multi-disciplinary perspective», in Appl Netw Sci, 2018.
PMID:30839779 - PMCID:PMC6214298
DOI:10.1007/s41109-018-0067-2
This is an Open Access resource - ↑ Viggiano A, Manara R, Conforti R, Paccone A, Secondulfo C, Lorusso L, Sbordone L, Di Salle F, Monda M, Tedeschi G, Esposito F, «Mastication induces long-term increases in blood perfusion of the trigeminal principal nucleus», in Neuroscience, Elsevier, 2015.
PMID:26477983
DOI:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.10.017 - ↑ Florio T, Capozzo A, Cellini R, Pizzuti G, Staderini EM, Scarnati E, «Unilateral lesions of the pedunculopontine nucleus do not alleviate subthalamic nucleus-mediated anticipatory responding in a delayed sensorimotor task in the rat», in Behav Brain Res, 2001.
PMID:11704255
DOI:10.1016/s0166-4328(01)00248-0 - ↑ de Boer RJ, Perelson AS, «Size and connectivity as emergent properties of a developing immune network», in J Theor Biol, 1991.
PMID:2062103
DOI:10.1016/s0022-5193(05)80313-3 - ↑ Iyer-Biswas S, Hayot F, Jayaprakash C, «Stochasticity of gene products from transcriptional pulsing», in Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys, 2009.
PMID:19391975
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.79.031911
This is an Open Access resource - ↑ Lewis ER, MacGregor RJ, «On indeterminism, chaos, and small number particle systems in the brain», in J Integr Neurosci, 2006.
PMID:16783870
DOI:10.1142/s0219635206001112 - ↑ Deriu F, Ortu E, Capobianco S, Giaconi E, Melis F, Aiello E, Rothwell JC, Tolu E, «Origin of sound-evoked EMG responses in human masseter muscles», in J Physiol, 2007.
PMID:17234698 - PMCID:PMC2075422
DOI:10.1113/jphysiol.2006.123240
This is an Open Access resource - ↑ Yamada K, Park H, Sato S, Onozuka M, Kubo K, Yamamoto T, «Dynorphin-A immunoreactive terminals on the neuronal somata of rat mesencephalic trigeminalnucleus», in Neurosci Lett, Elsevier Ireland, 2008.
PMID:18455871
DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2008.04.030 - ↑ Kondo K, Niino M, Shido K, «Dementia. A case-control study of Alzheimer's disease in Japan - significance of life-styles», 1994.
PMID:7866485
DOI:10.1159/000106741 - ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Kubo KY, Ichihashi Y, Kurata C, Iinuma M, Mori D, Katayama T, Miyake H, Fujiwara S, Tamura Y, «Masticatory function and cognitive function», in Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn, 2010.
PMID:21174943
DOI:10.2535/ofaj.87.135
This is an Open Access resource - ↑ Christensen J, «Effect of occlusion-raising procedures on the chewing system», in Dent Pract Dent Rec, 1970.
PMID:5266427 - ↑ 12.0 12.1 Ichihashi Y, Arakawa Y, Iinuma M, Tamura Y, Kubo KY, Iwaku F, Sato Y, Onozuka M, «Occlusal disharmony attenuates glucocorticoid negative feedback in aged SAMP8 mice», in Neurosci Lett, 2007.
PMID:17928141
DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2007.09.020 - ↑ Arakawa Y, Ichihashi Y, Iinuma M, Tamura Y, Iwaku F, Kubo KY, «Duration-dependent effects of the bite-raised condition on hippocampal function in SAMP8 mice», in Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn, 2007.
PMID:18186225
DOI:10.2535/ofaj.84.115
This is an Open Access resource - ↑ 14.0 14.1 Kubo KY, Yamada Y, Iinuma M, Iwaku F, Tamura Y, Watanabe K, Nakamura H, Onozuka M, «Occlusal disharmony induces spatial memory impairment and hippocampal neuron degeneration via stress in SAMP8 mice», in Neurosci Lett, Elsevier Ireland, 2007.
PMID:17207572
DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2006.12.020 - ↑ Kubo KY, Kojo A, Yamamoto T, Onozuka M, «The bite-raised condition in aged SAMP8 mice induces dendritic spine changes in the hippocampal region», in Neurosci Lett, 2008.
PMID:18614288
DOI:10.1016/j.neulet.2008.05.027 - ↑ Ichihashi Y, Saito N, Arakawa Y, Kurata C, Iinuma M, Tamura Y, Iwaku F, Kubo KY, «The bite-raised condition in aged SAMP8 mice reduces the expression of glucocorticoid receptors in the dorsal and ventral hippocampus», in Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn, 2008.
PMID:18464530
DOI:10.2535/ofaj.84.137
This is an Open Access resource - ↑ 17.0 17.1 Areso MP, Giralt MT, Sainz B, Prieto M, García-Vallejo P, Gómez FM, «Occlusal disharmonies modulate central catecholaminergic activity in the rat», in J Dent Res, 1999.
PMID:10371243
DOI:10.1177/00220345990780060301 - ↑ Yoshihara T, Matsumoto Y, Ogura T, «Occlusal disharmony affects plasma corticosterone and hypothalamic noradrenaline release in rats», in J Dent Res, 2001.
PMID:11808768
DOI:10.1177/00220345010800121301 - ↑ Gómez FM, Areso MP, Giralt MT, Sainz B, García-Vallejo P, «Effects of dopaminergic drugs, occlusal disharmonies, and chronic stress on non-functional masticatory activity in the rat, assessed by incisal attrition», in J Dent Res, 1998.
PMID:9649174
DOI:10.1177/00220345980770061001 - ↑ Feldman S, Weidenfeld J, «Glucocorticoid receptor antagonists in the hippocampus modify the negative feedback following neural stimuli», in Brain Res, Elsevier Science B.V., 1999.
PMID:10064785
DOI:10.1016/s0006-8993(99)01054-9 - ↑ Mascaro MB, Prosdócimi FC, Bittencourt JC, Elias CF, «Forebrain projections to brainstem nuclei involved in the control of mandibular movements in rats», in Eur J Oral Sci, 2009, São Paulo, Brazil.
PMID:20121930
DOI:10.1111/j.1600-0722.2009.00686.x - ↑ Shirasu M, Takahashi T, Yamamoto T, Itoh K, Sato S, Nakamura H, «Direct projections from the central amygdaloid nucleus to the mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus in rats», in Brain Res, 2011.
PMID:21640334
DOI:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.05.026 - ↑ Avivi-Arber L, Lee JC, Sessle BJ, «Dental Occlusal Changes Induce Motor Cortex Neuroplasticity», in J Dent Res, International & American Associations for Dental Research, 2015, Toronto, Canada.
PMID:26310722
DOI:10.1177/0022034515602478 - ↑ Dworkin SF, Huggins KH, Wilson L, Mancl L, Turner J, Massoth D, LeResche L, Truelove E, «A randomized clinical trial using research diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders-axis II to target clinic cases for a tailored self-care TMD treatment program», in J Orofac Pain, 2002.
PMID:11889659 - ↑ Farrar WB, «Differentiation of temporomandibular joint dysfunction to simplify treatment», in J Prosthet Dent, 1972.
PMID:4508486
DOI:10.1016/0022-3913(72)90113-8 - ↑ Farrar WB, «Controversial syndrome», in J Am Dent Assoc, Elsevier Inc, 1972.
PMID:4503595
DOI:10.14219/jada.archive.1972.0286 - ↑ Eversole LR, Machado L, «Temporomandibular joint internal derangements and associated neuromuscular disorders», in J Am Dent Assoc, 1985.
PMID:3882811
DOI:10.14219/jada.archive.1985.0283 - ↑ Storum KA, Bell WH, «The effect of physical rehabilitation on mandibular function after ramus osteotomies», in J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1986.
PMID:3456031
DOI:10.1016/0278-2391(86)90188-6 - ↑ Schiffman E, Anderson G, Fricton J, Burton K, Schellhas K, «Diagnostic criteria for intraarticular T.M. disorders», in Community Dent Oral Epidemiol, 1989.
PMID:2791516
DOI:10.1111/j.1600-0528.1989.tb00628.x - ↑ Phillips DJ Jr, Gelb M, Brown CR, Kinderknecht KE, Neff PA, Kirk WS Jr, Schellhas KP, Biggs JH 3rd, Williams B, «Guide to evaluation of permanent impairment of the temporomandibular joint», in Cranio, American Academy of Head, Neck and Facial Pain; American Academy of Orofacial Pain; American Academy of Pain Management; American College of Prosthodontists; American Equilibration Society and Society of Occlusal Studies; American Society of Maxillofacial Surgeons; American Society of Temporomandibular Joint Surgeons; International College of Cranio-mandibular Orthopedics; Society for Occlusal Studies, 1997.
PMID:9586521 - ↑ Talley RL, Murphy GJ, Smith SD, Baylin MA, Haden JL, «Standards for the history, examination, diagnosis, and treatment of temporomandibular disorders(TMD): a position paper», in Cranio, American Academy of Head, Neck and Facial Pain, 1990.
PMID:2098190
DOI:10.1080/08869634.1990.11678302 - ↑ Prayer Galletti S, Colonna MT, Meringolo P, «The psychological aspects of craniocervicomandibular pain dysfunction pathology», in Minerva Stomatol, 1990.
PMID:2398856 - ↑ Truelove EL, Sommers EE, LeResche L, Dworkin SF, Von Korff M, «Clinical diagnostic criteria for TMD. New classification permits multiple diagnoses», in J Am Dent Assoc, 1992.
PMID:1290490
DOI:10.14219/jada.archive.1992.0094 - ↑ Lobbezoo F, Visscher CM, Naeije M, «Some remarks on the RDC/TMD Validation Project: report of an IADR/Toronto-2008 workshop discussion», in J Oral Rehabil, Academic Centre for Dentistry Amsterdam (ACTA), 2010, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
PMID:20374440
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2842.2010.02091.x
particularly focusing on the field of the neurophysiology of the masticatory system